Table of Contents
The search engine optimization (SEO) industry has grown to massive proportions. And that’s because SEO is essential to every online business – publishers, local stores, and ecommerce giants alike. But that also means navigating best practices can be difficult. There’s so much to know. And not every best practice is relevant to every practitioner.
This SEO cheat sheet will help you focus on the most important aspects of on-page, off-page, and technical SEO – which are relevant to all businesses, no matter the industry. Whether you want to hire an SEO expert or plan to do the work yourself, refer back to this information as you make decisions along the way.
On-page SEO cheat sheet
On-page SEO encompasses all of the optimization that you do to your web content. It includes all of the content that users can see on your site and search engine results pages (SERPs).
This type of SEO accounts for the majority of all optimization techniques, meaning it’s likely what you’ll spend most of your time on. Here are seven of the most important on-page optimization areas that you should focus on for better SEO results.
Title tag
A title tag is the clickable headline for a listing in search results. It is the text that users click on to visit a website.
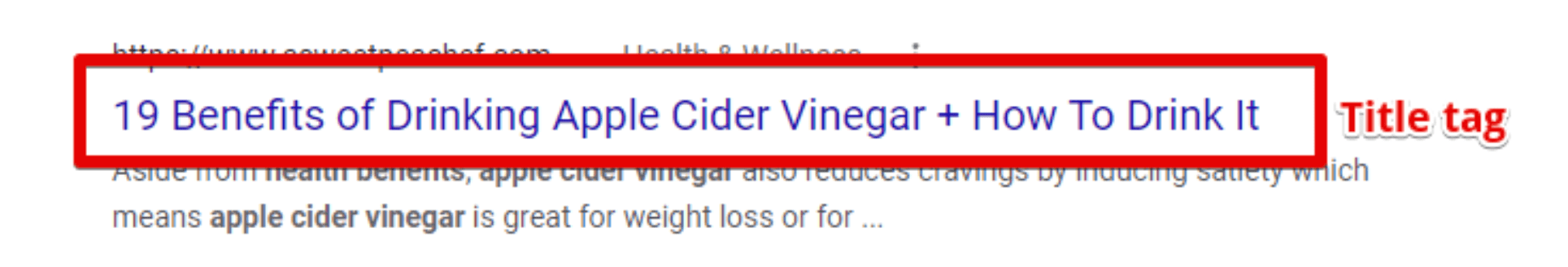
Your title tag should include your target keyword and should draw the user’s attention. A Backlinko study of more than five million search results found that title tags between 15 and 40 characters have higher click-through rates (CTR):
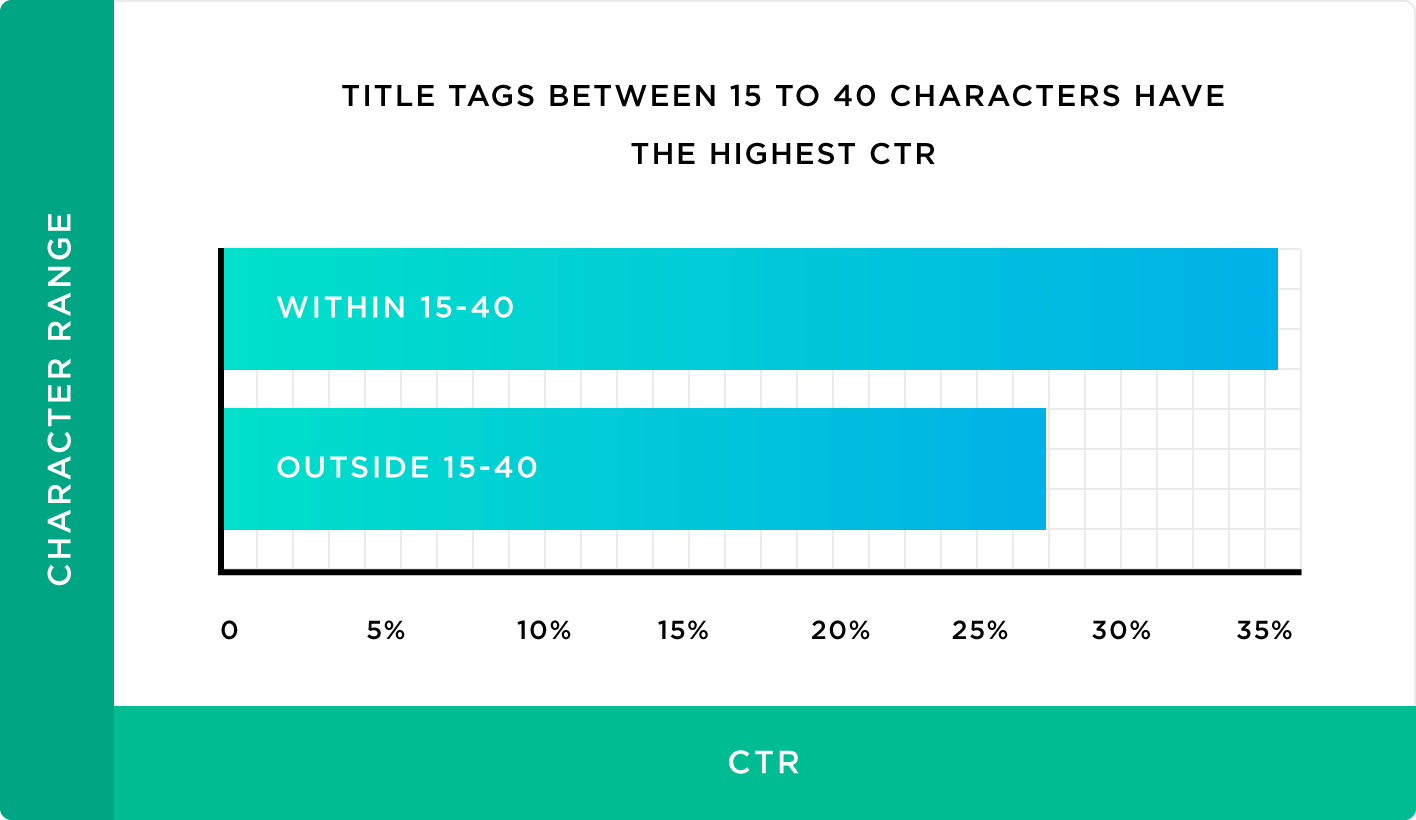
Remember, titles connect users to your web pages. Make sure your titles provide value. If they don’t explain the content or appeal to emotions like excitement or curiosity,
Headers
Headers organize content so that it’s easier to read. You can have as many headers as you want from H1 all the way to H6.
The only required header is the H1 tag which tells Google the main topic of your content. You can have multiple H1 tags, although it is most common to have just one.
Heading tags should:
- Describe the contents of each section
- Include relevant keywords
- Help users navigate a web page
It is most effective to write headers before you write your content. They’ll serve as a kind of outline. That way, you will know exactly which topics you want to touch on. This can speed up the writing process and improve the flow of your content as well.
Search intent
Google’s main goal is to provide a great user experience. That’s the number one thing the algorithm wants to offer through the content on SERPs.
The best way to do this is to satisfy search intent. This means making sure that your content answers the user’s search query – that it provides products, information, etc. that users are looking for.
There are four main types of user intent that explain why users are searching for a specific term:

To satisfy search intent you need to:
- Define your target audience’s pain point. What kind of solution do they want?
- Write your content with the correct format and tone. Use SERPs to discover what type of content is already ranking for your keywords. This will give you an idea of how to write your own.
- Produce high-quality content that includes comprehensive information, images (especially for products), and data for your audience.
This process is designed to move the user to the next stage in their search journey. Content that satisfies intent should either end the journey or point a user to a related web page.
Keywords
In SEO, keywords are the terms that users type into search engines. Each piece of content should be focused on one particular keyword or phrase. This ensures that your content only ranks for the term that you’ve based it around.

When incorporating keywords, here are some things you should know:
- Long-tail keywords typically have higher conversion rates than short-tail keywords.
- You should include your keyword throughout your web content. This includes in the body text, headers, alt text, file names, meta descriptions, and titles.
- Using your keyword too much is called “keyword stuffing.” It is a black-hat SEO technique that can result in a Google penalty.
If you don’t choose a primary keyword, your content will be very unlikely to rank. Google won’t be able to determine which terms it relates to. As a result, you will end up with a piece of content that ends up lost in the farthest SERPs where virtually no users go.
Meta description
Meta descriptions are the lines of text beneath title tags. Their purpose is to provide users with more information or context for the web page.
You’ll notice in this example that the meta description has been cut off in the search results. This is called truncation and it can happen when you use too many characters in your description.
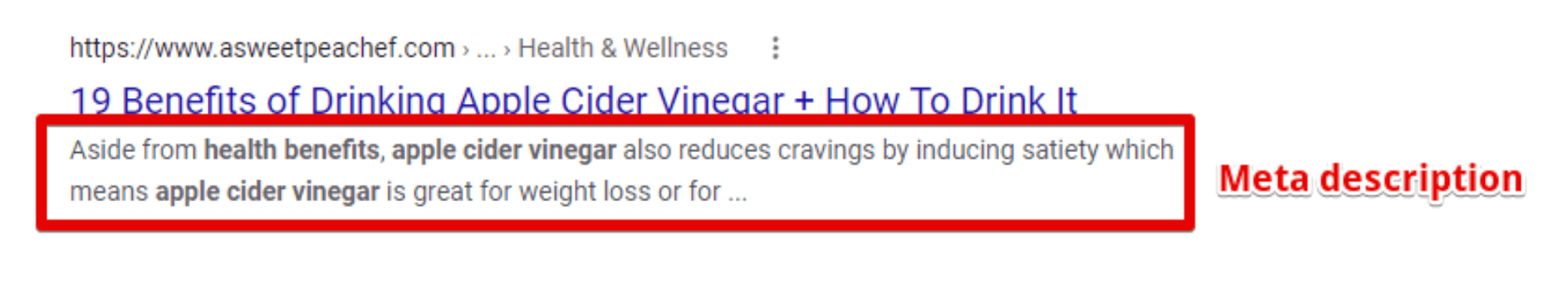
To avoid truncation, try to keep your descriptions to no more than 155-160 characters. When writing a meta description, be sure to include your target keyword and offer users additional information beyond what’s in the title. This ensures that you’ve used your space efficiently to provide as much context as possible.
Images
Images are commonly used to visually break up written content and to explain concepts in further detail. But they do take up a large amount of space if you don’t optimize them. This slows down your website, negatively impacting user experience. Since page speed is an official ranking factor, this can really hurt your search engine rankings.
Implementing these SEO best practices will ensure that your images don’t affect your page speed:
- Resize and compress images so their data files take up less space on your website.
- Delete fluff images that don’t add value to your content. This means using decorative photos sparingly. Only add images that help tell a story, explain a concept, etc.
- Use alt text to describe images to both visually impaired users and crawlers. Alt tags should be specific and contain a keyword (if possible).
- Change image file names to match the content of the image itself.
- Only use JPG, JNG, or WebP photos on your site. Other file types like DOC and PDF won’t load properly.
The overall goal of image SEO is to ensure that images have the most benefit to users with the smallest possible impact on site performance.
Internal linking
Internal links are links from one page on your website to another page on your website. They are important for multiple reasons:
- They help crawlers find new pieces of content on your website.
- They allow users to explore a topic in more depth.
- They pass link equity from page to page.
Here are some helpful tips for optimizing internal links:
- Write anchor text that includes the page’s primary keyword.
- Only link to relevant information for the topic you’re writing about.
- Avoid overuse of internal links. Google robots will typically crawl roughly 150 links per page.

With a dedicated link-building strategy, you can increase your site’s relevance within a particular niche. Be sure to avoid linking to missing, incomplete, or duplicate content. This can negatively affect your on-page SEO by creating a poor experience for site visitors.
Popular tools for on-page SEO
Since on-page SEO is a major component of any digital marketing strategy, there’s a lot to monitor. That’s why it’s helpful to take advantage of tools and plugins to automate certain tasks. These tools to help increase your organic search traffic without having to invest as much time into the process:
- Ahrefs Keyword Explorer: Find keyword opportunities, analyze current search rankings
- Google Search Console: Track SEO metrics
- Yoast SEO WordPress plugin: Manage redirects, meta tags, and internal links, optimize written content
- RankMath: Do SEO analysis tracking rankings; add structured data markup
- Google Keyword Planner: Discover new keywords and related terms
With these tools, you’ll save time by getting SEO tasks done more efficiently. If you want some more ideas of which tools to use, check out this free SEO tools guide.
Off-page SEO cheat sheet
Off-page SEO is any optimization tactic that occurs outside of your website. This can include a variety of locations like other industry-related websites and blogs, social media, user forums, and more.
The goal of off-page SEO is to build authority by means of backlinks. These techniques allow you to promote your content, widen your audience, and demonstrate how your content provides value to users.
Backlinks
Backlinks are links from another website to yours, also known as referring domains. Each backlink serves as a sort of upvote signaling that your content is worthwhile. Search engines look for backlinks to determine whether or not they should display your content to users.
Google looks for both the quality and quantity of backlinks you have. Getting links from authoritative sources is preferred, as those domains carry more weight. Still, you should aim to get backlinks from a variety of sources. These are some of the best ways to generate backlinks and build credibility within your niche:
- Write long-form content over short content.
- Create interesting and useful infographics.
- Guest post for relevant brands and/or bloggers.
- Publish proprietary data and research.
- Reach out to other brands and share your content as a replacement for broken links on their site.
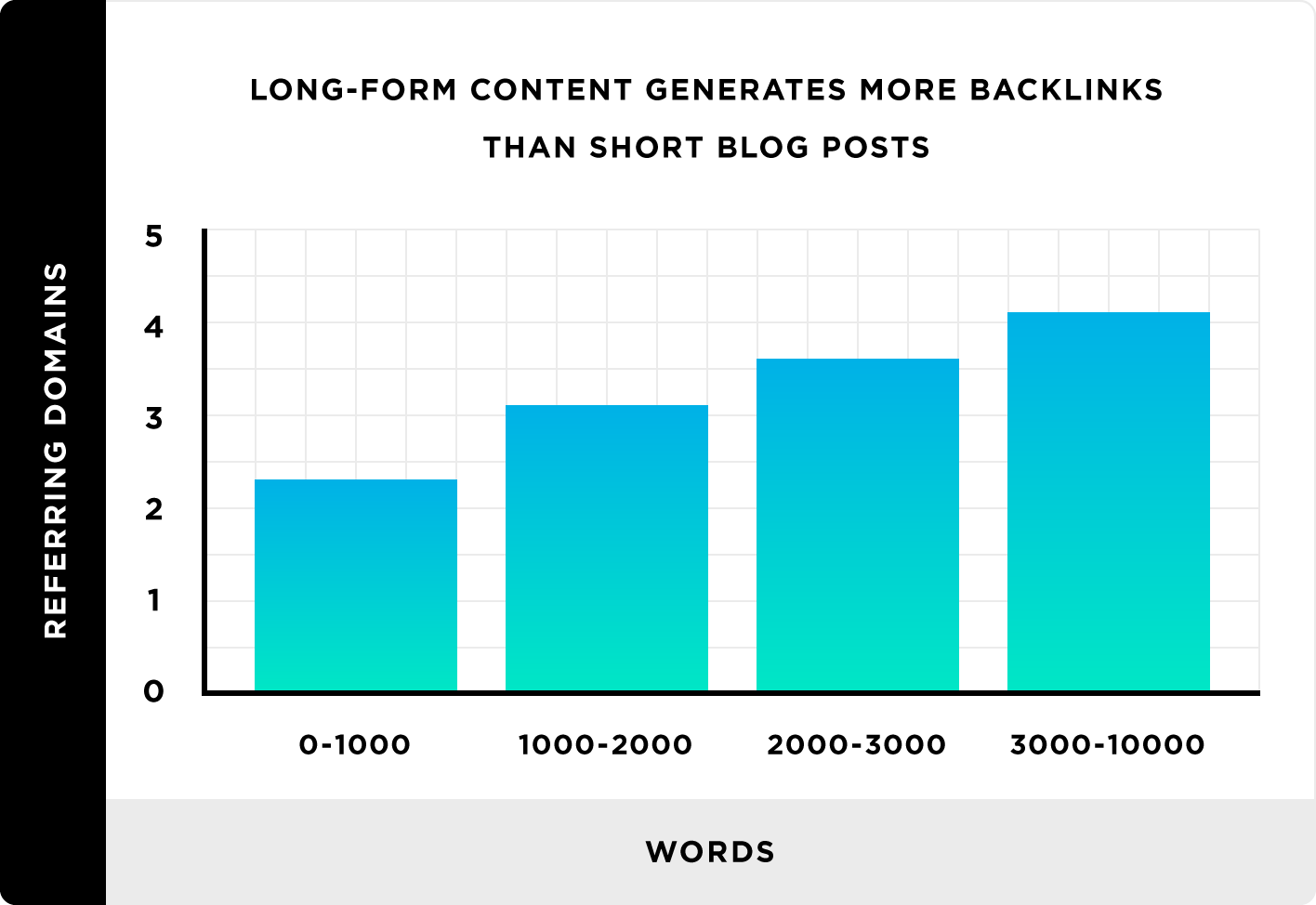
A key to earning backlinks is producing high-quality content. This starts by understanding your target audience’s needs and ensuring that what you’ve created is shareable.
Social media
Though social signals are not a Google ranking factor, you can use social media as an avenue for off-page SEO. Platforms like LinkedIn and Facebook are great places to build a following and share your content. When trying to earn website traffic and backlinks from social media, make sure to:
- Post consistently so users can rely on you for great content.
- Interact with your audience via comments sections.
- Write a great caption that makes users want to click on the post.
- Include your website or brand name, as well as your target keywords.
- Have your contact information easily accessible to users.
Social signals are a Bing ranking factor, so it’s important that you have at least one social media account where you can expand your audience. Not only will this help more users find your content, but it will also demonstrate how your brand provides consistent value.
Local SEO
For businesses with brick-and-mortar locations, local SEO is an important off-page SEO strategy. It involves making your brand accessible to users within your local area. Essential components of a well-executed local SEO strategy include:
- Setting up complete business profiles on Google My Business (GMB), Bing Places, and Apple Maps
- Targeting local keywords
- Creating a designated page for each physical store location you have
- Publishing and responding to customer reviews
- Making your contact information easy to find
- Building NAP citations within relevant directories
Local SEO is all about making sure that customers can find you. If you don’t optimize for search results in your local area, it’s likely that your competitors will win more customers.
Popular tools for off-page SEO
Here is a list of popular off-page SEO tools and how they can help you:
- BuzzStream: Connects local businesses together with backlink opportunities
- Ahrefs Site Explorer: Analyzes competitors’ search rankings and backlink profiles
- Semrush Backlinks Analytics Tool: Evaluates your backlinks and provides an authority score telling you how impactful those links are to your SEO
- BuzzSumo: Tracks the social media performance of content within your industry
- SE Ranking: Monitors your backlinks and local keyword rankings
Marketers use these tools to find new backlink opportunities, figure out what’s working for their competitors, and manage their SEO presence on social media (among other platforms). Overall, having an off-page SEO strategy is critical for building authority, improving brand perception – and for brick-and-mortars – driving foot traffic from local searchers.
Technical SEO cheat sheet
Technical SEO is the process of optimizing a website’s infrastructure – the background data files and code that allow the site to function as it shoudl. Technical SEO has two main purposes. First, it helps crawlers better understand site data. Second, it positively impacts user experience by creating a more efficient website.
Page speed
One of Google’s top-ranking factors is page speed, or the time it takes a web page to load. Page speed is important because it directly impacts user experience. The slower a website, the more likely users are to leave. Slow websites lead to poor SEO metric performance for things like bounce rate and number of pages visited.
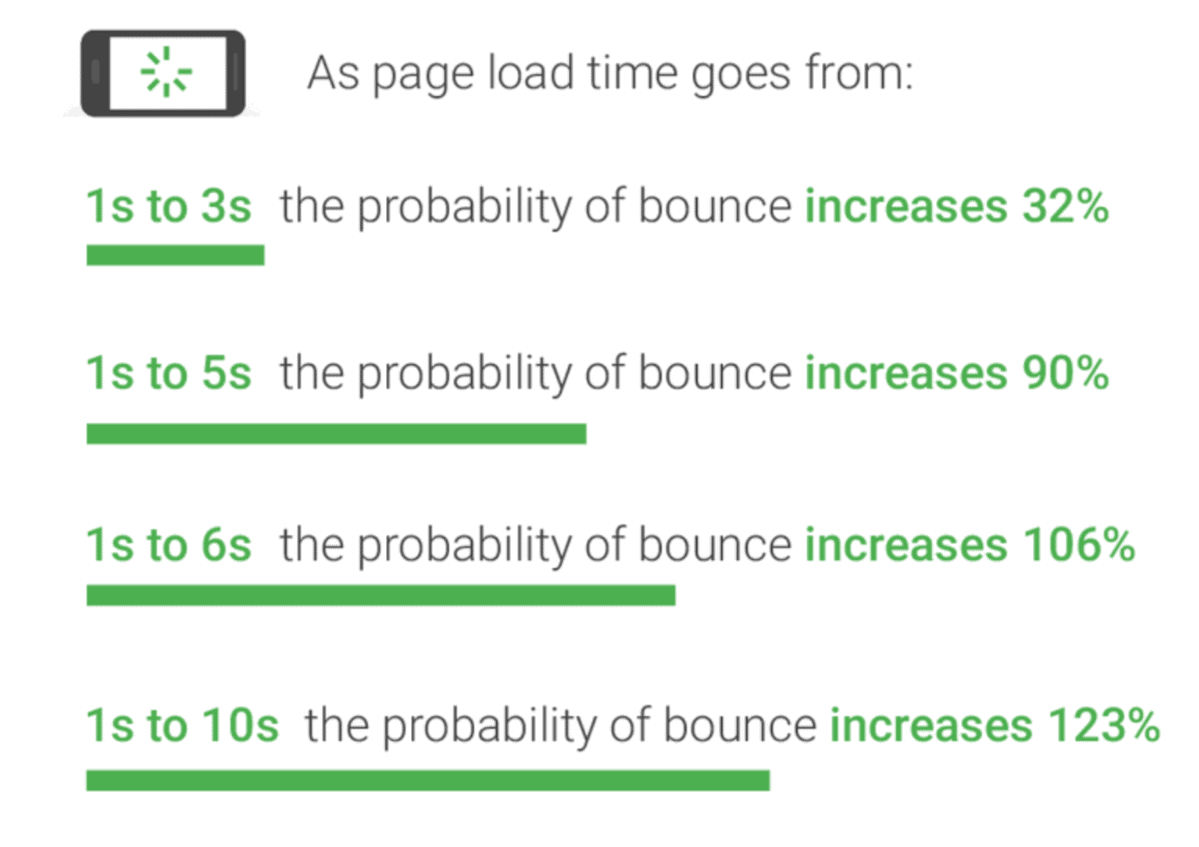
These are the top things you can do to make your website faster and more reliable:
- Minify your Javascript, CSS, and HTML code so only the essential information remains.
- Use a content delivery network (CDN) to speed up your server response time.
- Enable browser caching so pages load faster for repeat users.
- Compress and resize your images so they take up less space.
- Reduce redirects so users can get to pages quicker.
Certain elements like videos, music, etc. may slow down your site further. To increase speed, it’s important to be intentional with your page design and layout. Only includes these elements if they bring value to users.
Site structure
Organizing your site structure is essential to creating a good user experience. Without a clear hierarchy of web pages, topics, etc., users will have a harder time finding what they need. This ultimately leads to lower rankings.
Here are some tips for optimizing your site structure:
- Consider using the topic cluster model to organize content.
- Arrange your site in a hierarchy from broad to specific pages, and try to make 3 levels deep or less.
- Make all categories accessible through the homepage.
- Show breadcrumbs so users know where they are within the site.
- Add tags to web pages so you can have an index for all of your related pages.
A well-thought-out site structure helps Google understand your content. It also helps you manage posts so they don’t compete with each other in search results. The earlier you can define your site structure, the better.
Duplicate content
Duplicate content is identical or near-identical information on multiple web pages. Search engine crawlers may not always know what to do with duplicate content. When they come across it, crawlers often get confused about which version to show to users. As a result, the pieces of content compete against each other and neither one performs very well.
Manage your duplicate content by:
- Adding a canonical tag to the primary version of a web page.
- Deleting duplicate content entirely.
- Using 301 redirects to send users from a duplicate page to the main version.

These techniques will prevent crawler confusion as long as you properly implement them. Make sure to test any redirects or canonical tags before checking them off your to-do list.
Multilingual SEO
If you create content for a global audience, international SEO is essential. It is the process of optimizing web pages so they rank within the correct geographical locations.
This process includes several important technical SEO techniques such as:
- Adding hreflang tags to your content so Google knows what language it is in
- Using the correct currencies and slang terms in your content
- Doing proper market research on international audience segments
- Hosting content from a local IP address so it is more easily connected with foreign markets

You will need these tactics to reach an audience outside of your immediate geographical location. Before you implement any changes, however, make sure you plan carefully. If done incorrectly, multilingual SEO can actually damage your technical SEO and lead to a severe drop in rankings.
Mobile responsiveness
Each year, mobile SEO becomes increasingly important. More than 60% of all organic traffic comes from mobile devices now. And it’s for this reason that Google indexes mobile versions of web pages, not the desktop versions.
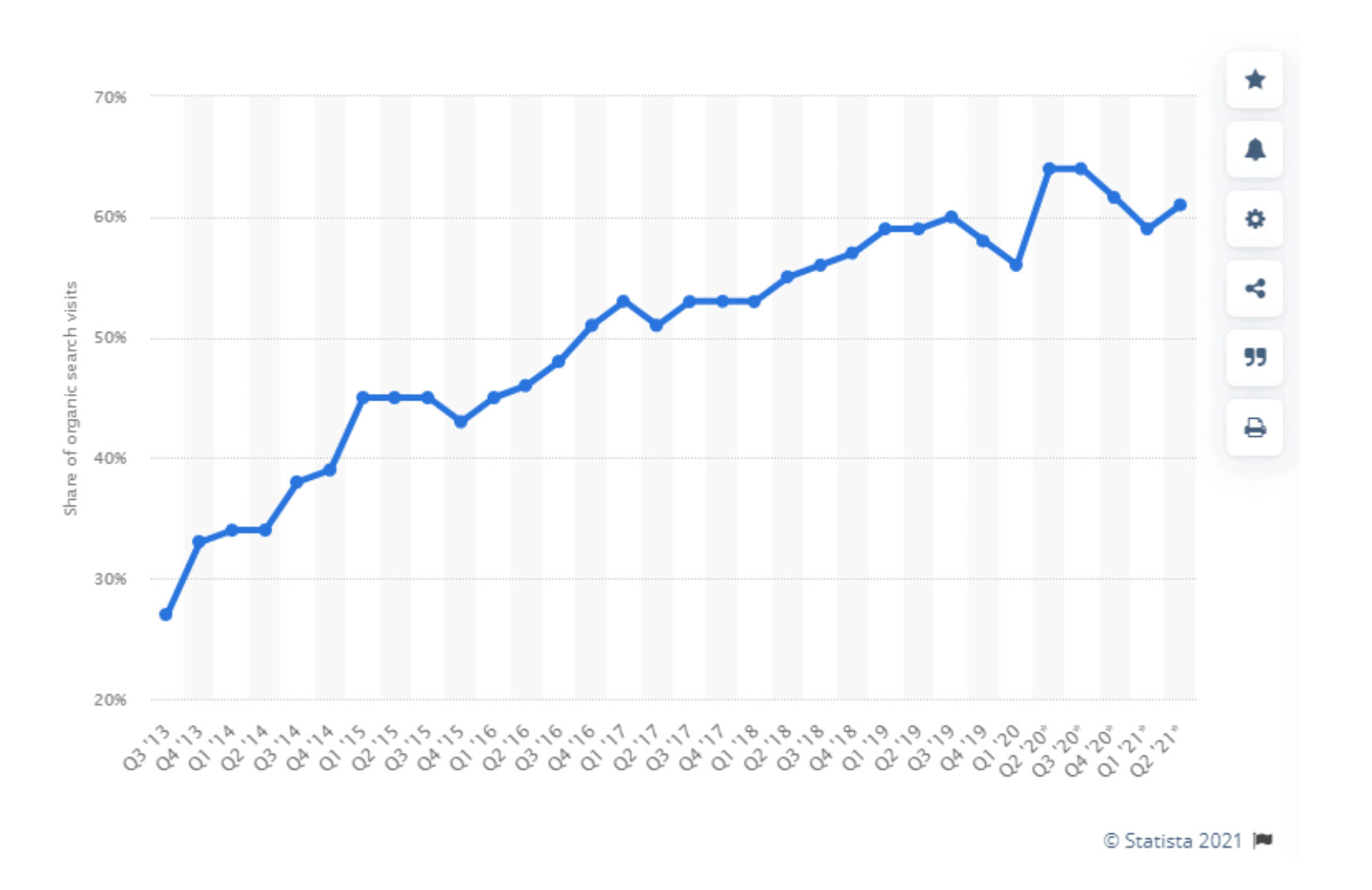
This is why you need to optimize your website for mobile devices. If you don’t, your site won’t provide a great user experience across all screens, and this can hurt search engine rankings.
Cater to mobile responsiveness by:
- Taking advantage of mobile responsive web design on platforms like WordPress and Wix
- Testing your content on both mobile and desktop
- Making elements like buttons and search boxes big enough for people to press with their fingers
- Writing meta descriptions that are 130 characters or less
- Keeping your title tags between 30 and 75 characters
Also make sure to resize or hide any content that is inessential to mobile users. This takes up valuable screen space, and most users look for the most important content at the top of the page. This is a rough template for how to organize your mobile content, if not your desktop content as well:

These techniques should make your mobile site more mobile-friendly.
XML sitemap
During the indexing process, crawlers find new web pages through internal links. One way to speed this process up is to submit an XML sitemap to search engines.
An XML sitemap is essentially a blueprint of all the URLs in your website. It helps search engines locate web pages that haven’t been indexed yet. Having this document will also allow you to keep track of your website content.
To make one, you can use a sitemap generator like the one from XML-Sitemaps or the Yoast SEO plugin. Once you’ve created your blueprint, don’t forget to submit it to Google and Bing. You can do this through Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools. Having this file available to crawlers can improve your rankings by ensuring that each piece of content is properly indexed.
Schema markup
Search algorithms have gotten much better at interpreting website data. But they still can’t understand content exactly the same way as humans. Schema markup is a semantic HTML vocabulary that you can use to help them out. It gives crawlers more context about your content.
Here are some tips for using schema (also known as structured data):
- Pick which type of schema you’re using before you start writing it.
- Use a tool like the Merkle JSON-LD Schema Markup Generator to create schema faster.
- Don’t forget to test your markup before adding it to your website.
From how-to content to authors, customer reviews, and more, schema makes it easier for search engines to analyze your web pages and rank them appropriately. Another benefit is that it can lead to rich snippets for your content.

With rich snippets, your pages will have higher potential CTRs because your SERP listings will provide more value to users. In the above example, instead of a standard listing, you get more information about these cookies: ratings, calories, baking time, and even an image.
Popular tools for technical SEO
Unlike on-page SEO, some aspects of technical SEO may require a deeper understanding of website development. But if you don’t have experience as a web developer, you can most likely find a tool to help you implement a change. Consider these options if you haven’t already:
- Screaming Frog: Finds technical issues on your site
- Google PageSpeed Insights: Tests your page speed and offers improvement suggestions
- Siteliner: Locates duplicate content issues
- Moz Pro: Crawls your site for things like missing title tags, redirect errors, meta noindex and nofollow issues, etc.
- Ryte Robots.txt Test Tool: Verify that your robots.txt file is working properly
Get a complimentary SEO audit
The SEO industry has grown to accommodate businesses that need help understanding and implementing SEO practices. With the right knowledge you can reach more customers, gain more authority in your niche, and generate more traffic and growht. This SEO cheat sheet will help you decide which areas to focus on so you can achieve these goals and more.
Want to see how you’re doing with SEO? Get an instant SEO audit below. Or, schedule a free consultation to see how intent SEO can boost search traffic revenue by 700%.
