Table of Contents
Google gets over 3.5 billion searches every day. To get a piece of that valuable traffic, you need a search engine optimization (SEO) strategy.
Search engine optimization is the process of improving web pages to make them more visible in search engines. For beginners, it can seem daunting. Fortunately, we’ve put together a Google SEO guide filled with proven SEO techniques to help you optimize content so it ranks higher in Google.
What is Google SEO?
Google SEO is SEO specifically for Google, the largest search engine in the world. Fortunately, optimizing for Google is also optimizing for other search engines — like Bing or Yahoo — because many of them follow the same principles as Google.
SEO is a process of optimizing three different aspects of a website and its content to make the website more likely to rank for different types of organic search. Organic means search that isn’t paid for (pay-per-click (PPC) is paid traffic).
The goal of SEO is to get your content to show up on a search engine results page (SERP) when someone types in a search term related to what your business does. Typing in a search term is called a search query. The image shows a SERP for the search term, “what is a thyroid.”
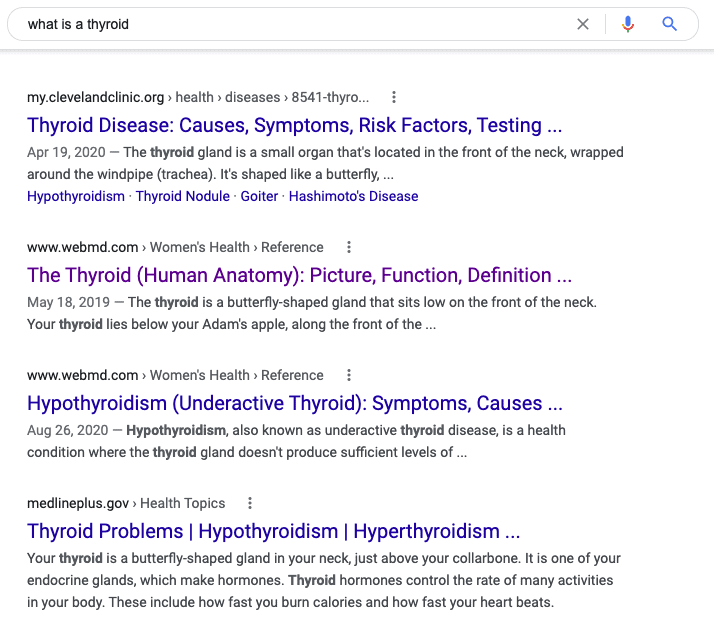
The results on the search are called organic search results — search results that Google has indexed without anyone paying for them. When someone clicks on a search result and goes to that page, it’s called organic traffic (as opposed to paid traffic).
To understand how to get organic traffic to your website, you need to understand all the different aspects of SEO. The three aspects of SEO are:
- Technical SEO
- On-page SEO
- Off-page SEO
This starter guide will explain each of these aspects to help you understand exactly what each aspect means and what you need to do for each one.
- Technical SEO refers to what you need to do to your website to make it easy for Google to find, crawl, and understand. It also refers to some aspects of the usability of your website (how good of a user experience your website provides).
- On-page SEO refers to everything you do on each page to help Google understand what your content is about. Creating content that is designed to rank on Google and be useful and valuable for searchers is called content marketing and is a form of digital marketing that requires an understanding of on-page SEO to be effective.
- Off-page SEO refers to actions you take to get other web pages to link to your pages. Mostly this refers to the process of building backlinks.
How does Google rank web pages?
Before Google ranks a page, it has to learn about the page to understand what it’s about. It needs to do this so that it can show the page to the right people when they search for something on Google.
It learns about the page through a process called “crawling.” Crawling is where a robot called a crawler explores each page on your website. It looks at aspects of each page, like the title tag, the alt text for the images (text that explains what an image is about), the filenames of the images, the meta description (text that explains what the page is about), and the rest of the text on the page.
It explores the internal links on your website to see what pages exist. It uses all this information to determine if this content should be shown to a searcher. This is the process of indexing. If it decides the content should go onto Google, it indexes the content.
Once the bots decide that your content should be served to a searcher, Google uses over 200 ranking factors to decide how high to rank the content on its index.
Black hat SEO vs white hat SEO vs gray hat SEO
Following Google’s guidelines is always recommended. When you follow Google’s guidelines to improve your page’s search engine ranking, you’re practicing white hat SEO.
Black hat SEO involves practices that disregard these guidelines. These tactics are often used as shortcuts to get content to rank faster or higher than normal. They may be effective in the short term, but they can also get you in trouble with Google, which means you can be penalized in search results or your content can even be deindexed (taken off of Google).
Gray hat SEO is a set of tactics that may or may not go against Google’s guidelines. They’re tactics that SEO experts aren’t all aligned on. These tactics can possibly work well and get your content indexed, but they might also result in ranking penalties (your content stops being ranked as highly).
You should try as much as possible to employ white hat SEO tactics and follow Google’s guidelines. This is the best way to keep your content on Google and keep it ranking.
A brief history of Google SEO updates
Google constantly updates its algorithms. In fact, it’s estimated that they update 500-600 times a year.
However, there have been some major updates over the years that have had profound impacts on online businesses and business websites in general. While Google has implemented major updates since it first launched in 1998, it’s most useful for you to understand the major updates in the past 10 years.
These are the major updates since 2011 and their effects:
- Panda—content quality became a ranking factor. Websites could no longer create low-quality content and expect to rank. Relevant content became critical to ranking. Websites with low-quality content or lots of duplicate content lost rankings.
- Venice—search results began taking your location into account when you searched for something. This is the beginning of modern local SEO and helped businesses to get more organic traffic from local searchers.
- Penguin—backlinks (links from another website to your website) were scrutinized for quality. Websites with lots of spammy, low-quality links were penalized (search volume for their ranked pages dropped and their rankings dropped). This hurt businesses that relied on black hat SEO techniques to get backlinks.
- Hummingbird—this update attempted to account for voice search and natural language. Rather than looking at just a few keywords in a sentence or a phrase, Google began looking at how all the words were related to each other. This helped businesses who weren’t the best at optimizing keywords to start ranking better.
- Pigeon—this update improved local search results and updated the degree to which location was taken into account for search queries. Businesses that relied on local search traffic benefitted.
- HTTPS/SSL—having HTTPS implemented on your website became a ranking factor. This increased in importance over time as many webmasters needed time to implement HTTPS on their website. Many businesses had to scramble to get HTTPS implemented.
- Mobilegeddon—because the majority of traffic started coming from mobile devices, Google began to prioritize mobile-friendly websites. Websites that were desktop-only began to see their search rankings dip.
- RankBrain—this machine learning update helped Google to better understand queries that it hadn’t seen before by comparing words it didn’t know to words it did know. Results for search queries became more accurate, helping businesses who weren’t the best at SEO or exact keyword matching.
- Possum—local search was improved in this update, leading many businesses to perform better in local search results.
- Speed update—page loading speed became a ranking factor. Websites that loaded slowly were penalized.
- Medic—some websites that provided medical information lost rankings as Google likely attempted to provide higher-quality medical information to searchers (and not just medical information from businesses).
- BERT—this major update improved the machine learning and natural language processing capabilities of Google. This helped a lot of businesses because Google became better at understanding the context of words on a page, not just the words themselves.
How to do Google SEO for your business
The three components of Google SEO are:
- On-page SEO
- Off-page SEO
- Technical SEO
On-page SEO
On-page SEO is everything you do on each web page. It mostly has to do with the content of your pages. This matters because every page on your website can be a landing page for searchers. Each page needs to be optimized so that it offers users everything they are looking for.
Keyword research
Keyword research is the process of figuring out what people are searching for in relation to your business. When someone uses Google, they type in a sentence or phrase. You can use keyword tools to learn what people are typing into Google. You can then create content that aligns with those keywords and that also aligns with your business goals.
High-quality content
High-quality content is content that covers a subject or topic completely, accurately, and without fluff. The user finds this content to be valuable, which means they feel like their question is being answered by the content.
Google prioritizes content that gives a user a complete answer. Google knows that this has happened because the searcher stops going back to the SERP. This is called “closing the loop” and is a ranking factor on Google.
High-quality content is also user-friendly. That means you’ve included headers to break sections into digestible chunks. Headers also help a searcher find content they’re searching for if they’re skimming.
High-quality content also has internal links, which are links from one page on your website to another page on your website. Internal links help searchers by giving them more information on a topic.
Internal links also help search engines to better understand how different pages on your website are connected to each other while also helping crawlers to find new pages on your website.
Meta titles and descriptions
Meta titles and meta descriptions make up a search listing on a search result. The image shows a search listing.
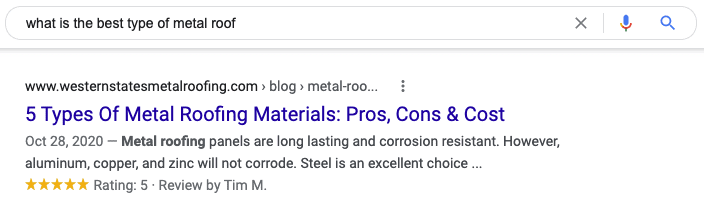
The large text on the top is the meta title. A meta title is the title of your page that shows up on a Google SERP. The meta description is the smaller text underneath. This description helps searchers to understand what a page is about.
A good meta title draws the reader in while also answering their question. In the image, the search term, “what is the best type of metal roof,” is closely matched by the title in terms of keywords, but what draws the reader in is the end of the title—pros, cons, and cost.
A searcher who is looking for the best type of metal roof is likely going to be interested in these three aspects of a metal roof, and therefore is going to be likely to click.
Your meta title, likely even more than your meta description, affects your click-through rate (CTR). Though a title tag can be up to 60 characters, title tags between 15 and 40 characters have a higher CTR. Other factors can heavily affect CTR—title tags that have a question in them, for example, have a 14.1% higher CTR than pages that don’t.
CTR matters because you want searchers on your page. The more people click, the more searchers consume your content, the more likely you are to generate leads or sales through your content).
Meta descriptions also affect CTR. Pages with meta descriptions get 5.8% more clicks than those without. A meta description should be below 160 characters and should include keywords. You can see the keywords highlighted in the example. You should also have a call to action at the end of the meta description, like “click to learn more.”
Internal linking
Internal links are links between one page on your website and another page on your website. These links are made of text combined with HTML markup. The text is called anchor text. The image shows a link with HTML applied.

Internal links are important to the user experience because they help searchers find new and related content, or dive deeper into a particular topic. They’re important to Google because crawlers will use them to find and rank your pages, and it can also help Google understand how the pages on your website relate to each other.
When you include internal links from old content to new content, Google is able to more quickly find new content on your website and decide if it should be ranked. Internally linking from high-ranking pages to low-ranking pages can also help those pages rank higher.
Off-page SEO
Off-page SEO is a collection of methods of getting other websites to link to pages on your website. Links from other websites to yours are called backlinks, and they help Google decide how high-quality your content is. When high-quality websites link to your content, Google sees your content as having authority, and therefore more potentially valuable to a searcher.
Guest blogging
One SEO tip that you’ve probably heard of is to guest blog regularly. Guest blogging is where you write a blog post for another website and include links back to your website.
Guest blogging can cost money as some sites charge you to put a blog post on their website, but other websites will do it for free—or even pay you to write for them.
Guest blogging gets your content and website in front of the audience of another website. It can bring you traffic from this new audience, and it also might result in members of this audience linking their content back to yours. This provides an opportunity for new backlinks from other sources.
Any links from the guest blog post back to your website also have value, especially if you’re guest blogging on a website that has good domain authority, so guest blogging can be an excellent way of generating quality backlinks.
Social media marketing
Social media links are not considered backlinks by Google, but social media marketing, similar to guest blogging, will get your content in front of a wider audience. As a result, you have a better chance of getting backlinks from this wider audience. Not to mention, studies have shown a correlation between high-ranking posts and high social engagement.
Brand partnerships
When you guest blog for another website or share their content on social media, over time, there’s an opportunity for partnership with that brand. Brand partnerships are valuable because they give you access to that brand’s audience. They may also refer clients/customers to you.
Link-building strategies
There are a number of link-building strategies that focus on finding opportunities on other websites to get a backlink. For example, you might reach out to a website that has broken links on a page and suggest they replace the broken links with a link to your page. Or, you may try to get listed on relevant online directories. You can find more link-building strategies here.
Local SEO
Local SEO is the process of optimizing your website for local searchers. A few major components of local SEO are:
- Setting up a Google My Business page
- Encouraging reviews
- Getting backlinks
- Optimizing for mobile
Learn more about local SEO here.
Technical SEO
Technical SEO is what you do to improve your website’s infrastructure. This makes your website more user-friendly, and it also makes it so that Google can more easily understand what your website is about. Some aspects of technical SEO are ranking factors, like page loading speed, so they’re not just a good idea to implement—they’re critical to getting higher rankings.
XML sitemap
An XML sitemap is a list of all the pages on your website. Google uses a sitemap to find new and existing pages on your website so that it can crawl them.
A sitemap gives Google a place where it can regularly check for new pages. Otherwise, Google will only find new pages by crawling your website regularly, so it may take longer for new pages to rank. You can submit your sitemap to Google through Google Search Console.
Creating a sitemap is simple. If you have a WordPress website, you can use a plugin like Yoast, which will automatically generate sitemaps for you. You can also use sitemap generators to create a sitemap for you.
The image shows an example of an XML sitemap.
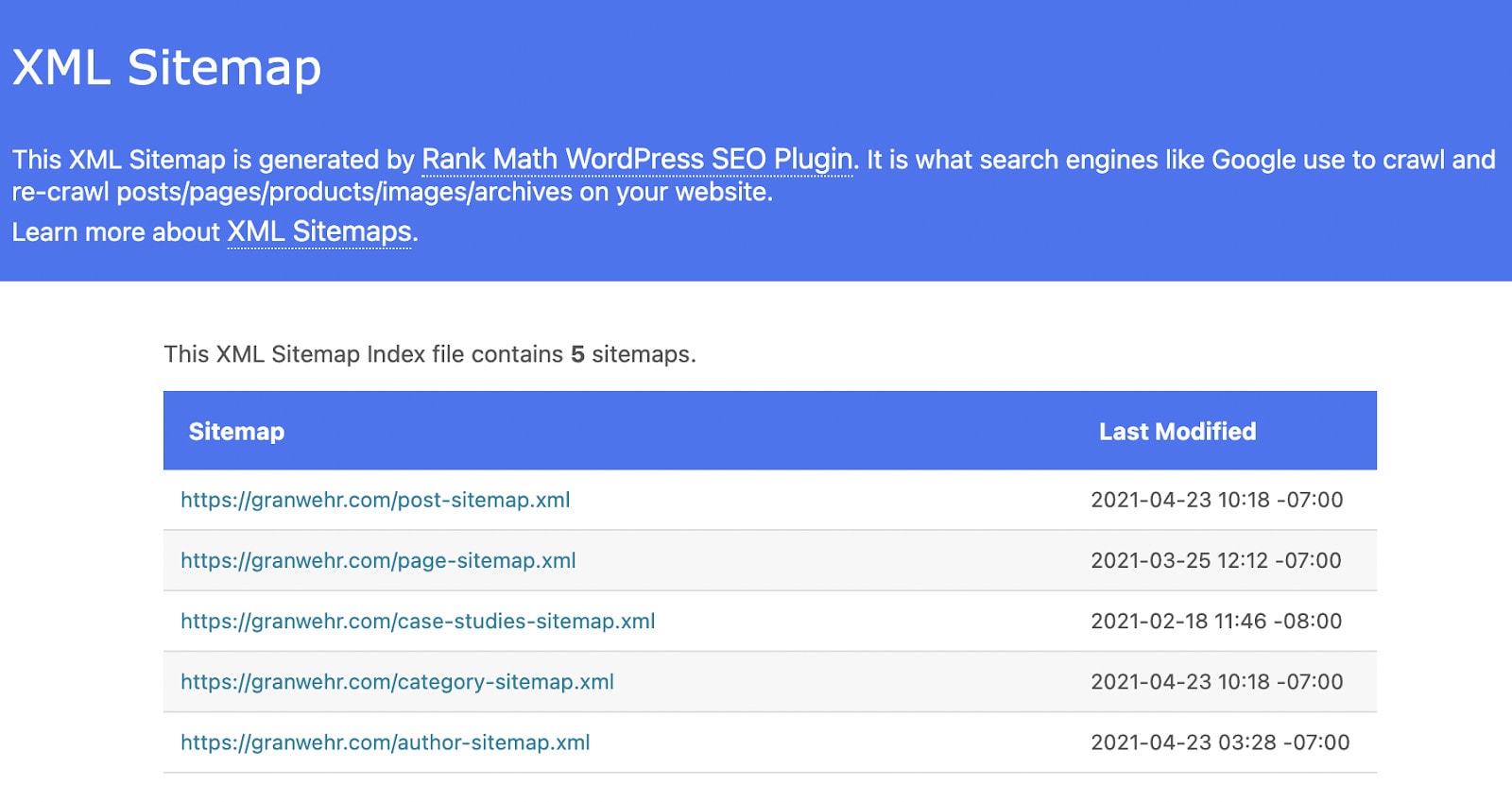
Robots.txt file
Your robots.txt file is used to tell Google not to crawl certain pages on your website. For example, you might intentionally have duplicate content on your website. You might not want to use a canonical tag for one reason or another (a canonical tag tells Google which content to index and which to ignore)—you might instead want to keep Google from crawling all those pages entirely.
You might also have content that is behind a paywall that you want to keep off of Google. Robots.txt is one way to keep that content from showing up for free on Google.
Page speed
Page loading speed is a ranking factor. You want to have pages loading on your website in under 3 seconds because otherwise you will lose searchers. In fact, 1 in 4 visitors will abandon your website if it takes more than 4 seconds to load.

Page load speed is critical to a good user experience, and ultimately, to generating leads and sales. You can check your page load speed here.
SEO-friendly URLs
SEO-friendly URLs are URLs that are short and include your main targeted keyword phrase. This makes them both easy for users and search engines to understand. A study by Backlinko also found that shorter URLs tended to rank better than long URLs.
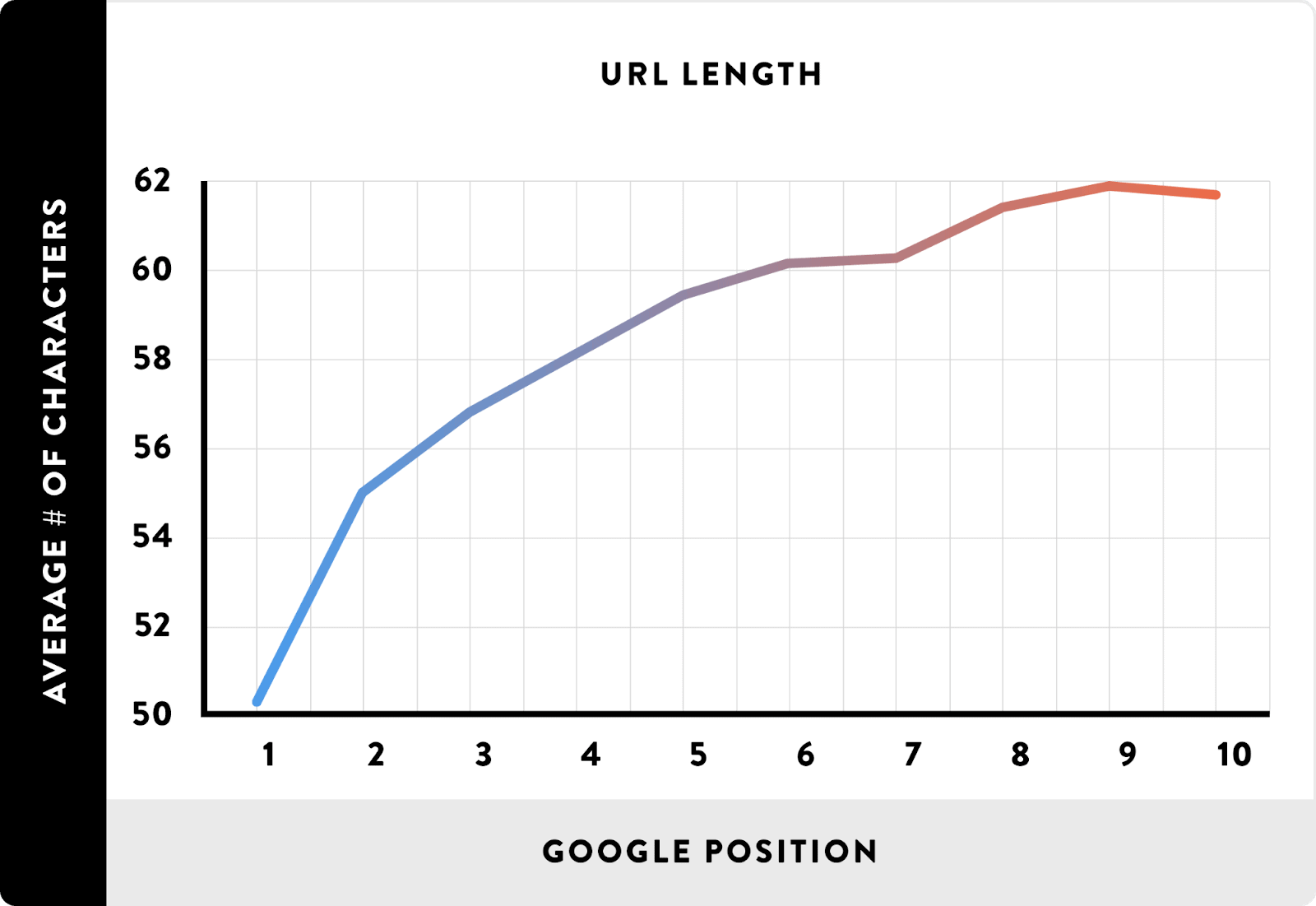
Search engines use URLs to try to understand what a page is about, so you want the URLs to be clear by only including keywords (if possible).
That may be one reason longer URLs struggle to rank—when they’re filled with a mishmash of numbers, letters, and symbols, they are harder for searchers to understand (they don’t know what they’re clicking on), and they’re harder for search engines to understand because they don’t have keywords in them. The search engines are forced to use other signals to try to understand what a page is about, leading to a page being less likely to rank.
Mobile-friendliness
Google indexes the mobile version of your website before it indexes the desktop version of your website. Mobile-first indexing means that you need to have a mobile-friendly website that adjusts to all screen sizes while remaining usable (the text can still be read, videos can still be easily clicked on, images are appropriately sized, etc.). Being mobile-friendly is a major ranking factor—it’s not something you can ignore.
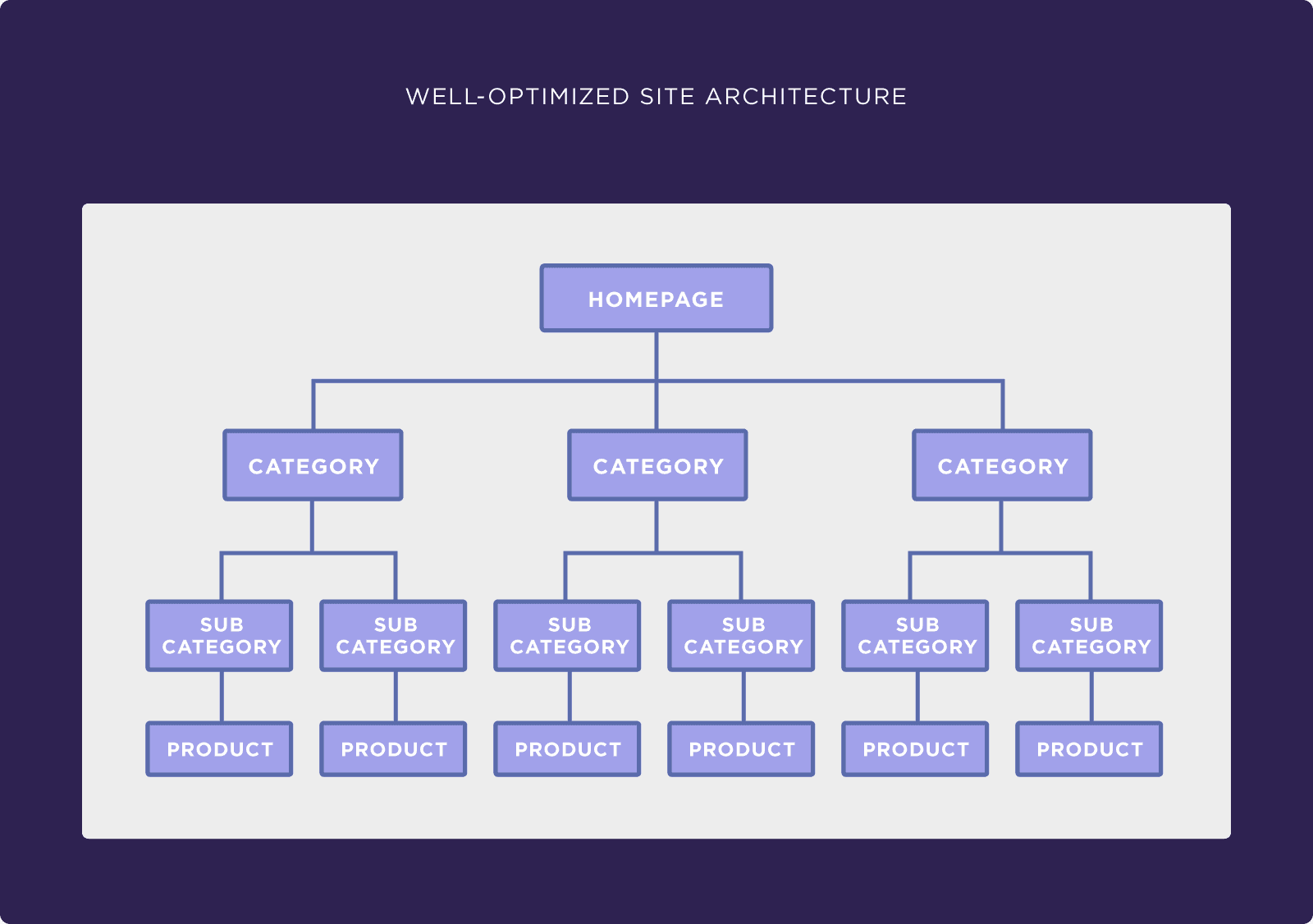
Optimized site hierarchy
A simple site hierarchy is good for both searchers and Google. It helps searchers to more easily find the content they’re looking for, and it helps Google to more easily understand the topics and pages and how they relate to each other. The image shows a simple site hierarchy.
Google SEO tools
There are many tools you can use for Google SEO—here are just a few:
- Google Analytics
- Google Search Console
- Keyword research tools
- Website audit tools
- Local SEO tools
- Content optimization tools
Find an extensive list of SEO software here.
Get a complimentary SEO audit
Now that you have a better understanding of how Google SEO works, you can start optimizing your website and your content for the biggest search engine on the planet. You don’t need to be an SEO expert to start ranking higher and generating more traffic, leads, and sales through Google.
Want to see how you’re doing with SEO? Get an instant SEO audit below. Or, schedule a free consultation to see how intent SEO can boost search traffic revenue by 700%.
