Table of Contents
A 2019 survey found that 70% of marketers gain more sales from search engine optimization (SEO) than paid advertising. And with more businesses flocking to the online space each year, creativity and unique content have become more important than ever for staying ahead of the SEO competition.
Google’s algorithm can now analyze content on a sophisticated level, understanding the context of a web page rather than just its literal words. As such, marketers now turn to an approach called semantic SEO to make their pages stand out. This strategy focuses on the development of user-friendly yet more complex content that approaches its main topic in a comprehensive and engaging way.
What is semantic SEO?
Semantic SEO is the process of producing content that is centered around an entire topic. Rather than targeting specific keywords, semantic content focuses more on answering the “why” behind a search term.
“Semantics” refers to the study of meaning in language. The goal behind this type of digital marketing is to provide more relevant information to searchers. Semantic SEO requires webmasters to understand user search intent. The ultimate goal is to create web pages that provide the right information, from the right angle, in the right format.
How is semantic SEO different from traditional SEO?
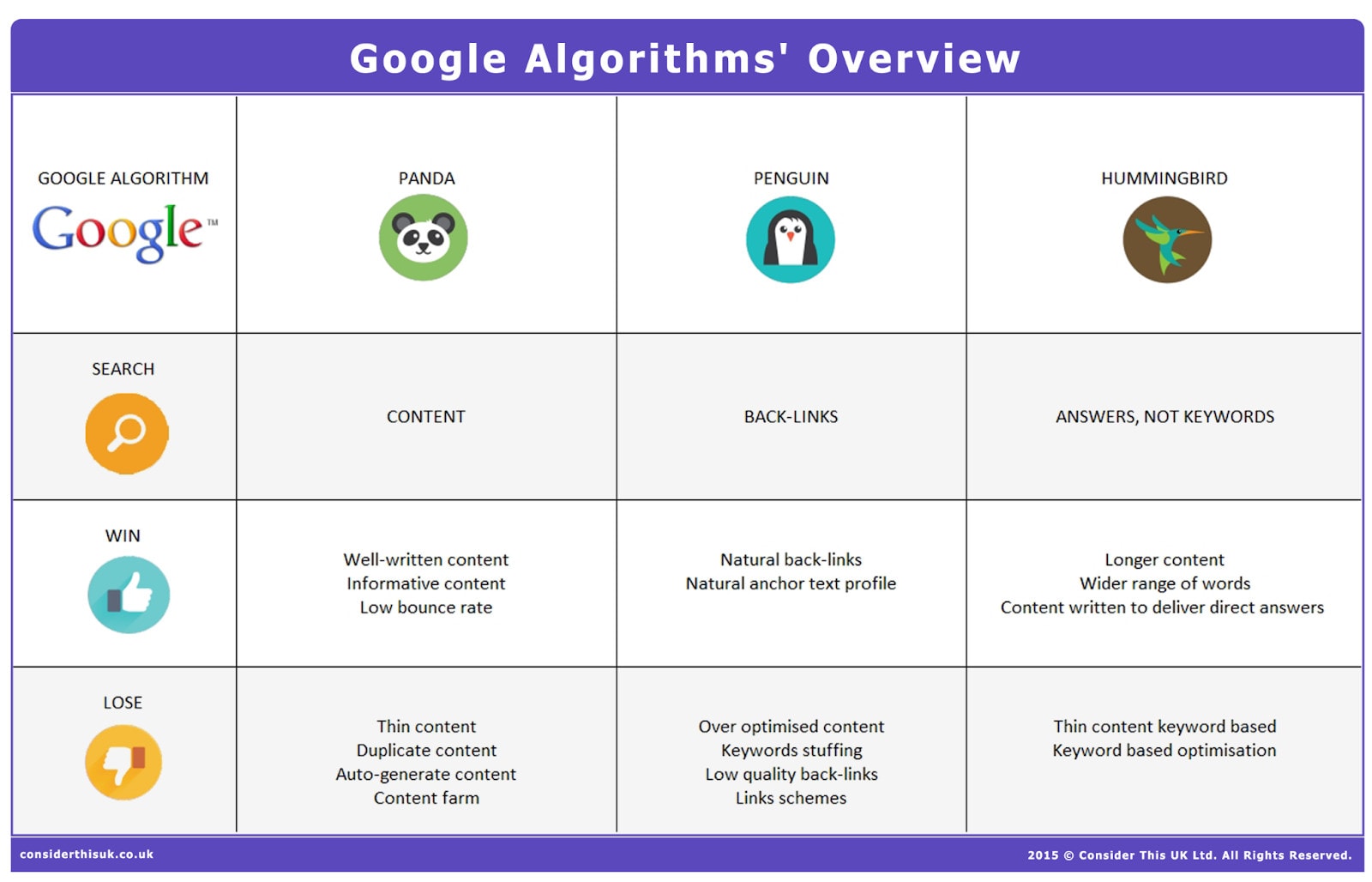
In the past, Google used keywords to determine the topic of a web page. Traditional SEO consisted primarily of including relevant keywords throughout the content. They were placed everywhere – header, title, description, etc. – so that Google could understand the content’s main topic.
In 2013, Google rolled out an algorithm update called Hummingbird. When this happened, crawlers gained the ability to read, analyze, and understand the overall theme of a page without relying on keywords alone. According to Moz, Hummingbird helped improve Google’s Knowledge Graph results, creating a better user experience in the process.
After this update, SEOs had to reevaluate their content and make it align with user search intent.
Now, semantic search optimization is essential for content marketing. If your web pages don’t address both the how and why behind a search term, they most likely won’t earn a top spot in search engine results pages (SERPs).
Why is semantic SEO important?
Marketers need to do semantic SEO because it ensures that they create the most relevant content possible. Search engines are constantly rearranging SERPs to accommodate user needs. Targeting the intent of a search makes your web page as user-focused as possible.
For example, say you’re an ecommerce store that sells face masks and you’re trying to rank for the keyword “face masks for travel.” You could create product pages that use the keyword in titles and descriptions, but this isn’t what users are looking for when they search “face masks for travel.”
How do we know that? Because when we search “face masks for travel,” the first SERP shows many blog posts that rank the best face masks for travel. That means Google, through data collection and user testing, has found that the most high-performing pages for this search are ranking blog posts.
That means you’ll probably have a better chance at ranking for this term by creating a “best of” or “top 10” blog post, or contributing a similar blog post (that includes your product) to a publisher with more SEO authority, or even reaching out to the creators of the current top-ranking lists and suggesting they add your product.
If you had created content just based on the keyword, you might’ve tried to create a product page. But by researching the context of this search, you’re able to use semantic SEO to create the most relevant topics and subtopics on your page for users.
Like Wikipedia information, semantic SEO content is organized more according to the context of the web page as it applies to the user. Rather than categorizing based on simple keywords, Google now understands how pieces of content apply to users in different ways. A semantic SEO strategy is meaning-driven, creating better web pages that can rank for a larger variety of search terms.
How to do semantic SEO
Learning how to do semantic SEO takes time and thoughtful planning. That’s because the process is a little bit more labor-intensive than basic optimization. You have to remember to keep user intent at the center of your entire SEO strategy.
Follow these steps for impactful semantic SEO. At the end of the process, you’ll have intent-driven content that provides value to the user. This can generate better rankings, increased organic traffic, and more conversions.
Start with keywords
Although semantic SEO approaches content from a different angle, it still uses keywords to provide context clues. Incorporating keywords is essential for conveying the most specific search query that you’re targeting.
Start your keyword research with a broad term like “closet organization.”
You’ll find all sorts of resources on this subject. You can use your current knowledge or interests to narrow down the topic.
For example, you could choose “closet organization for busy moms,” which further defines the topic and audience.
Long-tail keywords are very important to semantic SEO because they are typically more descriptive than general words or phrases. As far as rankings go, long-tail keyword content tends to have lower traffic but higher conversion rates.
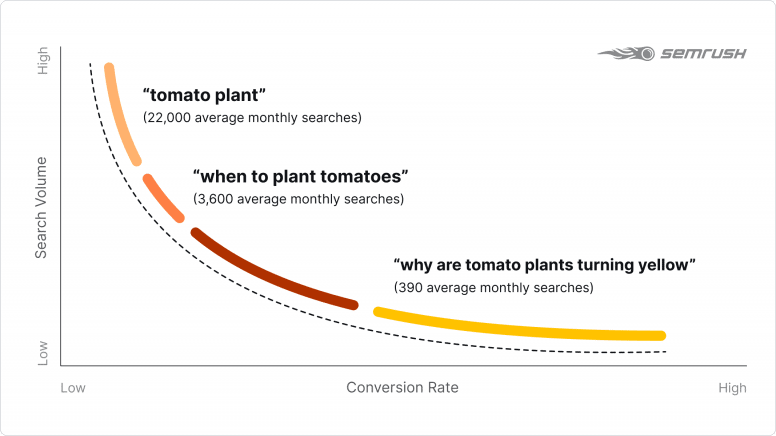
You can also target latent semantic indexing (LSI) keywords. Google relies on these types of keywords to understand web pages in a more complex way.
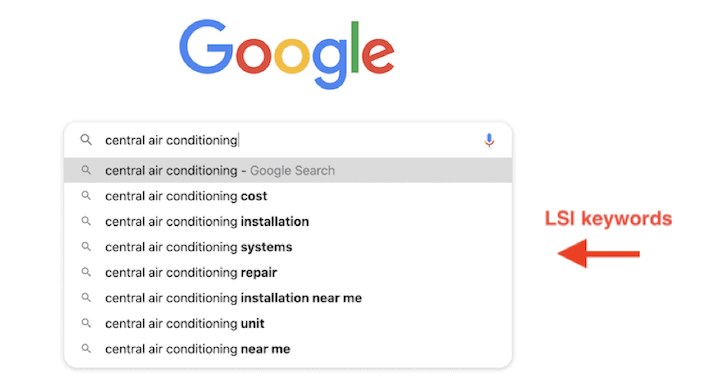
Having LSI terms in your content will assure Google of the main topic. When Google feels confident about a page’s subject matter, it is more likely to give it a higher ranking. Use the Google Keyword Planner to find popular search terms and generate ideas for new content on your website. This can save you a good amount of time if you have a hard time coming up with topics on your own.
Study the SERPs
The next thing you’ll want to do is go to the SERPs for more information. Google’s current listings can tell you a lot about what type of content to make. Input your keywords in the search bar and take note of what comes up.
The top-ranking post is titled “Busy Mom Closet Organizing Tips.” You can see the full use of keywords in both the title tag and meta description:
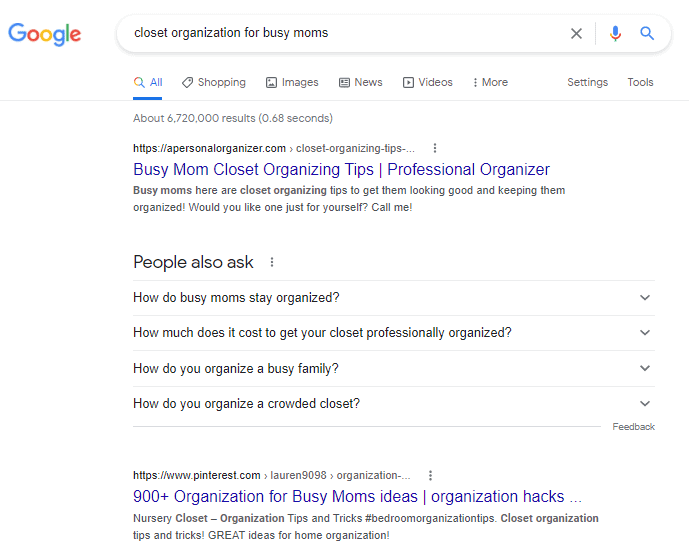
Notice that the top two most relevant results included all keywords and provided a unique selling point:
- First post USP: Content from a professional organizer
- Second post USP: More than 900 ideas
The “related searches” box gives you many different keyword alternatives. Study the verbiage in these queries:
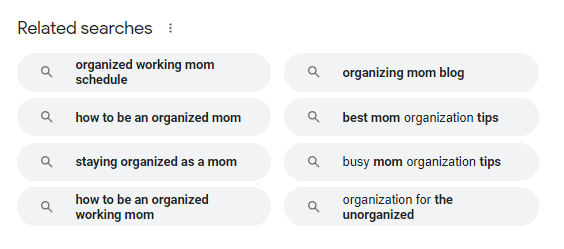
From this example, it’s clear that users are looking for tips and how-to content.
Studying the SERPs provides you with synonyms and other keyword opportunities in your niche while also revealing the user’s intent. In other words, you get a better idea of why someone was searching for your keywords and what they were hoping to find.
Determine intent
As you research your topic, you need to determine user search intent by answering these questions:
- What is the motivating factor behind these search terms?
- What type of content is the user looking for?
Again, the first page of search results will give you some clues. If there is a featured snippet, you can use that to find out the best format for your content.
Consider this featured snippet for the search term “closet organization tips:”
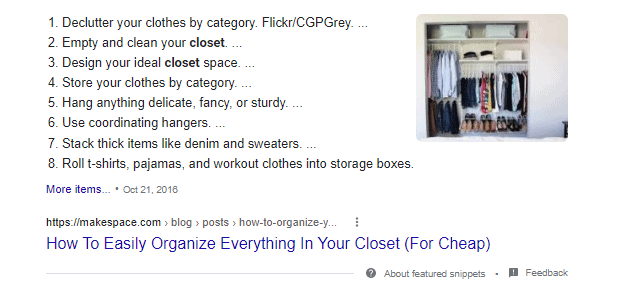
From this top result, you can tell that the search engine wants content in a list format. Check the “People also ask” box for more information on user intent:
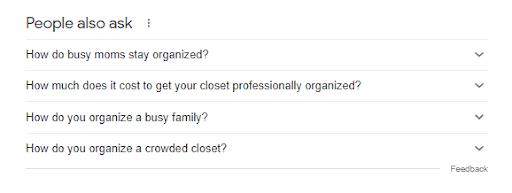
This information tells you that users are struggling to remain organized because they have families to take care of. Since all of the user queries start with “how,” you can assume that they want actionable content. They are looking for a web page to tell them the best methods for staying organized.
You’ll also see that a major pain point is the stress that comes with organization. That’s why some of the top results include words like “hacks” and “stress-free:”
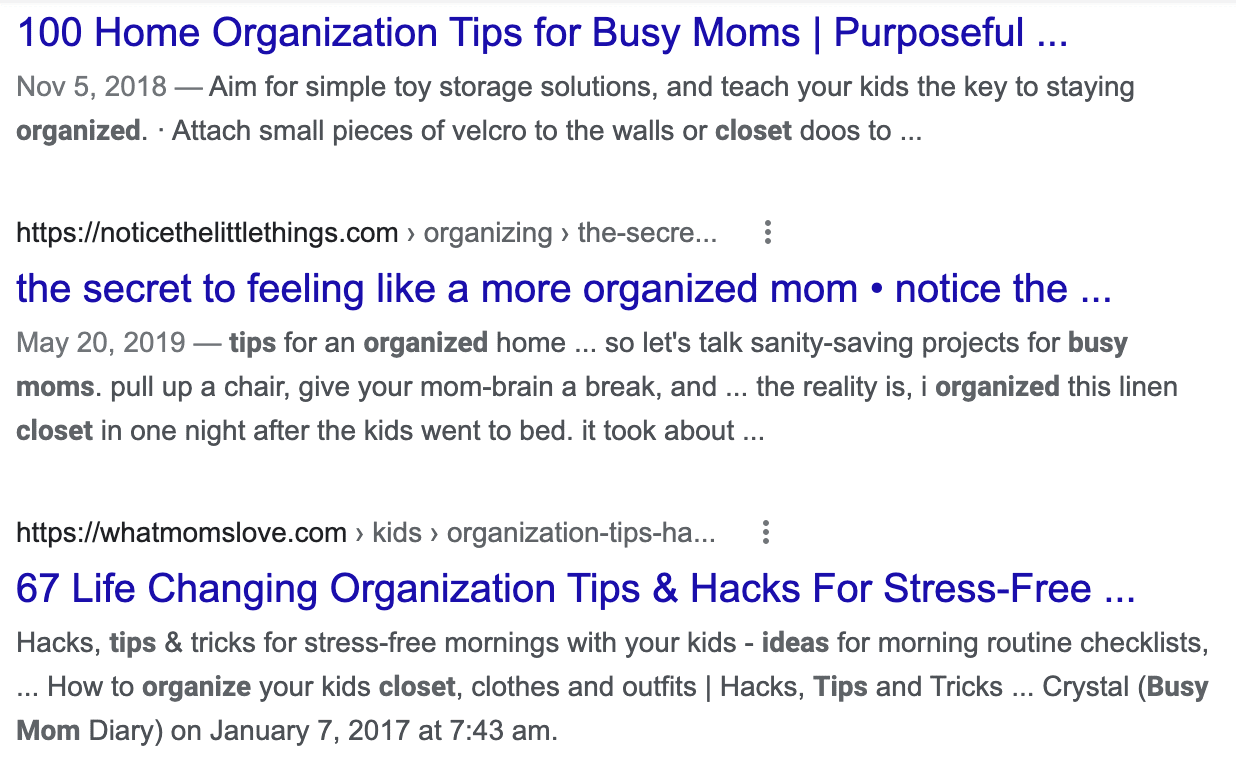
Browsing through the top pieces of content for style and tone will help you develop your own content. Oftentimes, you can identify common elements between the top results. What are they? What seems to be the consistent format or information? Knowing this will make you better-informed to create top-notch content.
Create high-quality content
A search engine’s goal is to find the highest-quality content possible. Some results maintain a top ranking for years because they provide the very best information that users can find.
When it comes to SEO, great content is comprehensive. This can mean many things, like:
- Discussing a topic in-depth
- Featuring relevant multimedia components (charts, videos, audio, images, etc.)
- Covering users’ major pain points
- Including proper citations and references (when applicable)
- Listing all the details of a product in-full
Content has to satisfy user intent in order to rank highly:
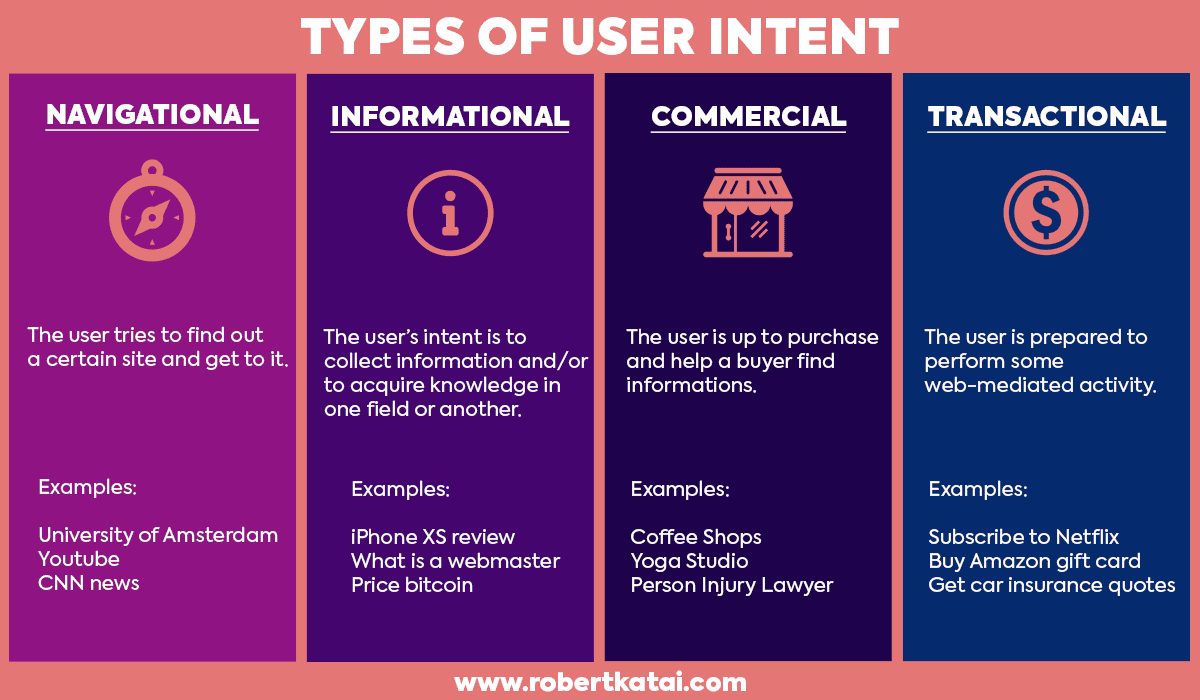
Always address user intent with both the writing and format of your content. The web page should predict where the user wants to go next. For example, if you create a rankings list of the best closet organization products, you need to add links in case the user wants to purchase them.
In your content, make an effort to answer the “People also ask” questions that you found in your initial keyword research. That way, the search engine may display excerpts from your web page for each of those drop-down options.
The overall point of high-quality content is that users find everything they’re looking for in one place. In other words, they don’t return to the SERP and repeat the search process all over again.
Optimize the user experience
Besides the written and visual content, you should also take into account the user’s experience on the page. It’s no secret that user experience affects your search rankings, with more than half of users saying web design impacts brand perception.

There are several things you can do to create a better user experience on your website, including:
- Create an intuitive site structure
- Organize your content with subheadings
- Keep paragraphs short
- Use internal linking
- Create a great meta title and description
- Include semantically related phrases
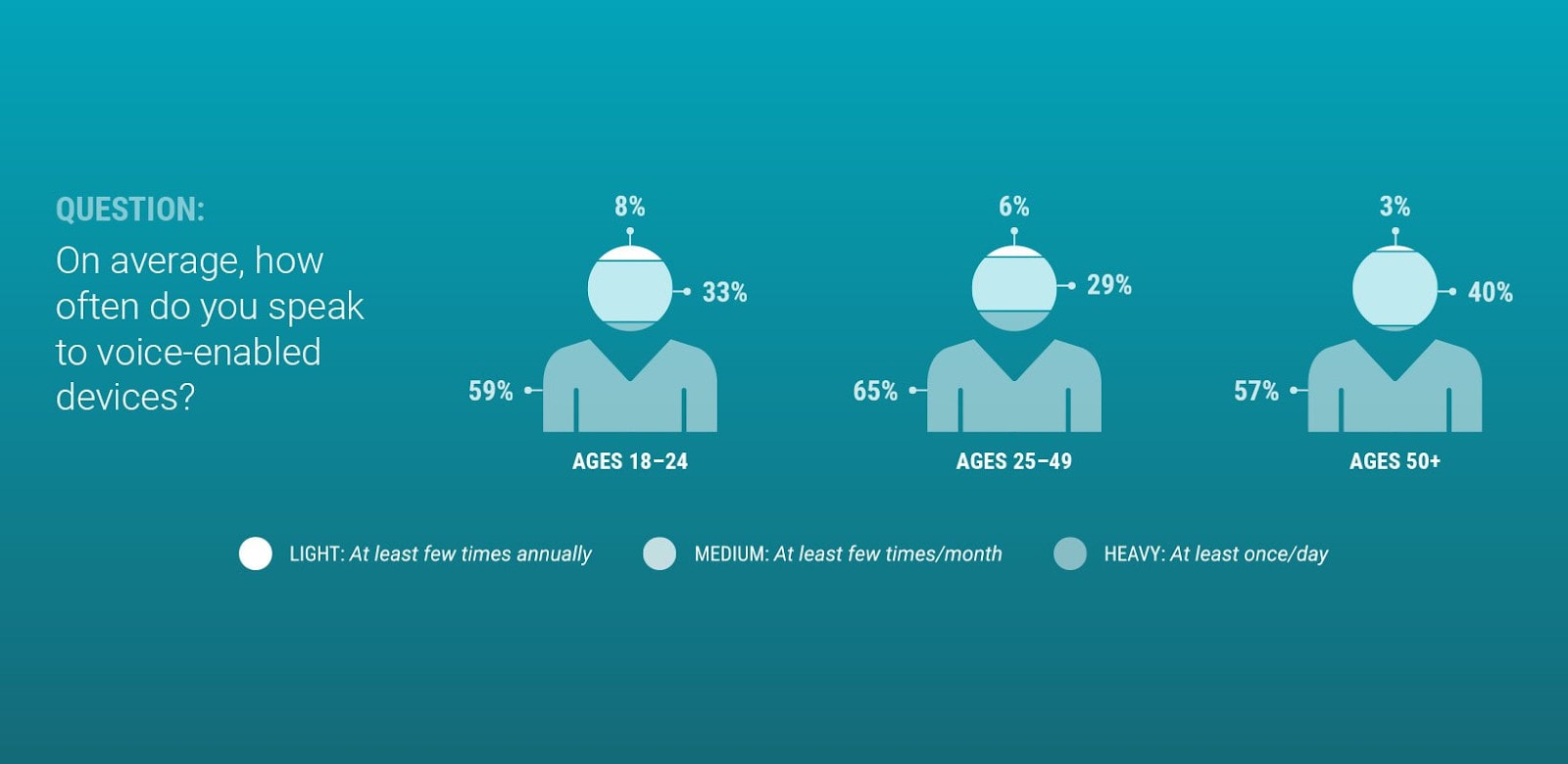
- Optimize for voice search

Popular content management systems like WordPress and Wix have responsive design capabilities. These help you build a user-friendly website for both mobile and desktop devices.
Another way to improve the user experience is to write in a way that’s easy to understand. Google’s RankBrain algorithm uses machine learning technology to understand and rank web pages. It is an important update that has led to the rise of semantic search engine results. RankBrain has natural language processing capabilities that allow it to understand content on a deeper level.
More people are using voice search powered by artificial intelligence (AI) technology each year.
This, coupled with the strength of RankBrain’s semantic language analysis, means that you should always write for your reader, not the search engine.
Build links
Just like a traditional approach, semantic SEO requires a link-building strategy. Search engines interpret backlinks as a sign of your site’s credibility and your content’s relevance. They remain one of the most important ranking factors for Google.
Build your backlink profile by:
- Targeting broken links on competing websites
- Answering questions on forums
- Writing guest posts for other blogs
- Doing industry-leading research
- Publishing case studies
- Partnering with other brands
- Creating shareable infographics and images
- Converting unlinked mentions into referrals
- Using influencer marketing
- Having an active social media account
A 2020 Ahrefs study found that many web pages have zero referrals from other websites:
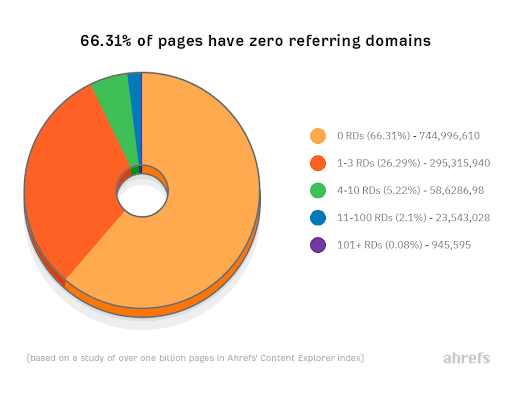
Are your web pages part of this majority? Use some of the tactics above to set yourself apart from the other two-thirds of web pages and to have better brand awareness.
Optimize technical SEO factors
Once you’ve created and published your semantic web content, you want to implement technical SEO on your website. Here are some of the most important optimization strategies for the backend of your content:
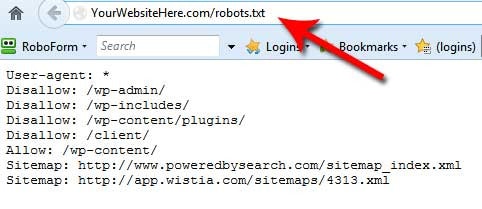
1. Robots.txt file: This is a file that tells the crawlers how to index certain pages, including which pages they can and can’t index.
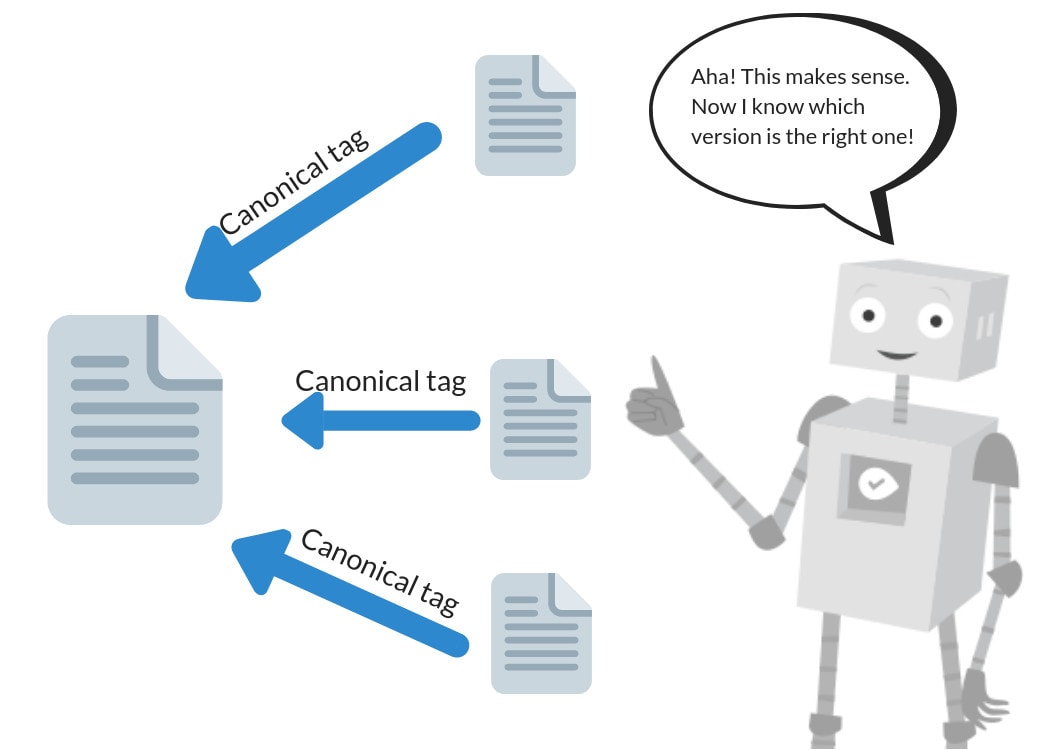
2. Canonical tags: These are tags in your code that help distinguish duplicate pieces of content.
3. Schema markup: It is HTML code that describes pieces of information within your content to the search engine. This can help you win results in the Google Knowledge Graph and can be found at schema.org.
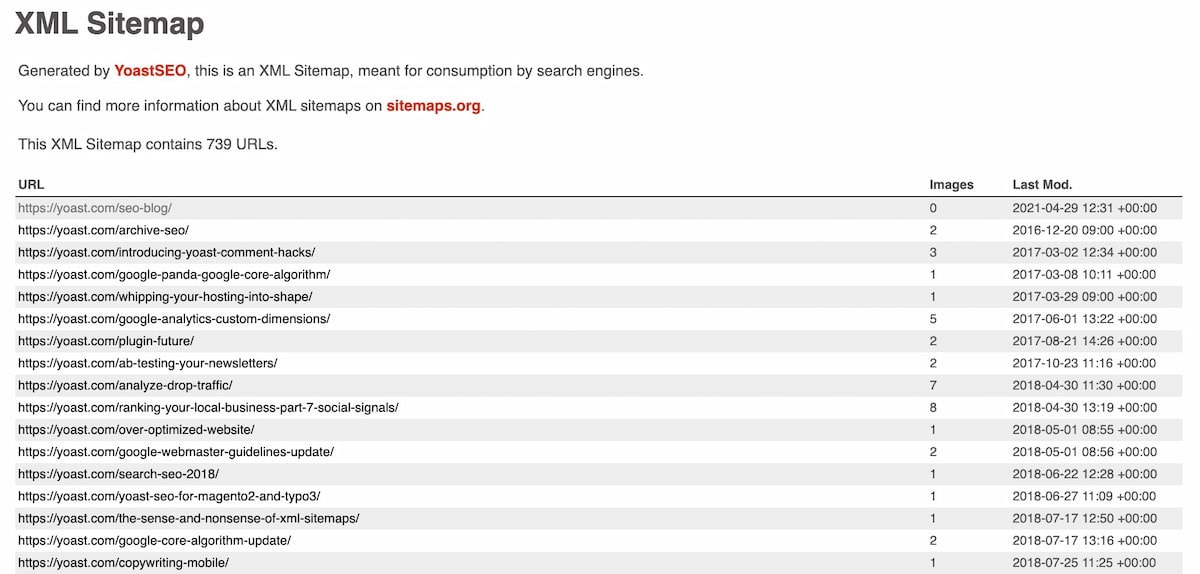
4. XML sitemap: It is a blueprint of all the pages on your website, and it helps crawlers find your content easier.
There are several other technical SEO techniques you can implement. Ensuring the functionality of your site improves your performance with the Google search algorithm. This is because it enhances the overall user experience.
Get a complimentary SEO audit
If you want to increase the ranking potential of your content, adopt a semantic SEO strategy. This approach will align your content strategy with the needs of the user. This can make you better at developing high-quality web pages that rank higher for more search queries.
Want to see how you’re doing with SEO? Get an instant SEO audit below. Or, schedule a free consultation to see how intent SEO can boost search traffic revenue by 700%.
