Table of Contents
Now that nearly 40% of all global ecommerce traffic comes from search, having an ecommerce SEO strategy is no longer a luxury. It’s a requirement for every business.
With $4.5 billion on the line, how do you get your ecommerce site in front of the countless search engine users looking for products like yours?
What is ecommerce SEO?
Ecommerce SEO (search engine optimization) refers to the process of improving an ecommerce website to make it more visible on search engine results pages (SERPs). It involves tactics like link building, content marketing, keyword research, and more.
With more visibility in search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo comes more organic search traffic to your ecommerce store, which means more potential customers. And since SEO is a low-cost marketing channel, unlike PPC (pay-per-click) advertising which requires continued investment, you can significantly boost sales opportunities without the high cost to your business.
How to use ecommerce SEO to earn more customers
Ecommerce SEO isn’t just a cost-effective way to earn traffic, it’s also a marketing strategy that can deliver higher ROI over time with relatively little maintenance. Here are some of the most important ecommerce SEO best practices you can implement to earn more customers.
Ensure relevance with keyword research
When someone types a search query into Google, an algorithm analyzes countless pieces of content to determine which are the most relevant to the search. They appear on page one in descending order from most to least relevant.
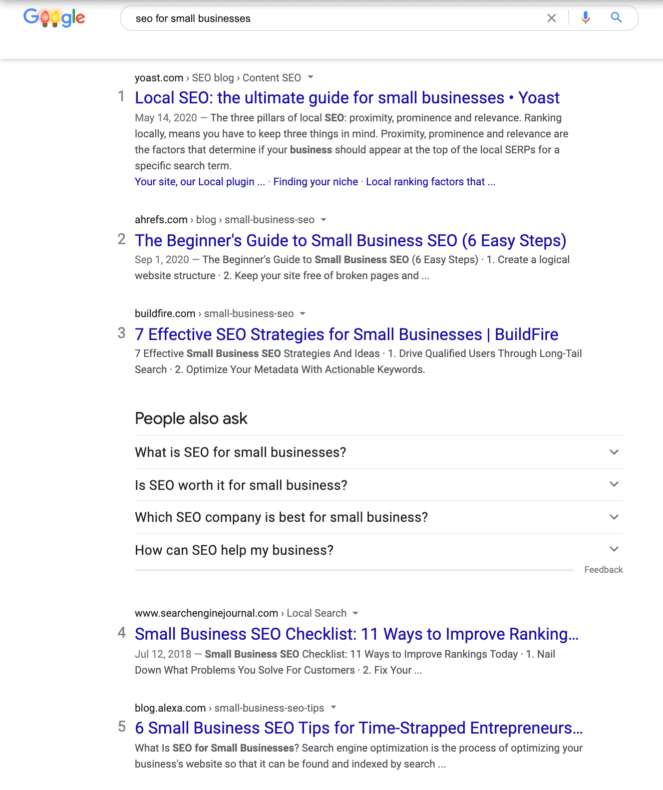
One of the key ways Google’s algorithm organizes this content is by looking for keywords related to the query in important places on a web page. That’s why you should be doing extensive keyword research.
Keyword research is what helps you find out the kinds of words prospects are using to search for your product. Once you know these keywords, you can include them in your content, along with related words and phrases, to signal to Google that you have content relevant to the user’s search.
To develop a list of keyword ideas, you can use tools like Google Search Console, Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs, Moz, SEMrush, and others. These will not only help you find keywords your visitors are using to search for your product, but they’ll also tell you how often those keywords get searched, how competitive they are to rank for, and much more.
Attract visitors with high-quality content marketing
Keyword research isn’t just to help you include the right words in the right places on your web pages — it’s also one of the foundations of a good content marketing strategy. To draw visitors to your website, you have to be able to create content that satisfies their searches. By discovering the terms they search for, you can position yourself to better answer these questions.
If, for example, if you’re an ecommerce business that sells children’s jewelry, you might want to try to appear on search engine results pages for the search terms “necklaces for kids” or “rings for small fingers.” Other searches like “how to size my finger for a ring,” or “what’s the difference between gold and gold-filled?” might also be queries that bring valuable traffic to your site.

Knowing this, you can create content to satisfy these searchers with product pages, blog posts, category pages, videos, FAQs, etc. Each page should have a single focus keyword. If you already have a lot of pages, start with your highest-value pages (look in Google Analytics for the revenue each page is bringing in), optimize for a focus keyword term, and work your way down.
Focus on search intent
The first page of Google search results is reserved for web pages that best satisfy the searcher because that’s what Google wants to do: It wants to serve its users the highest-quality, most comprehensive sources of information.
To satisfy the searcher, you have to have a deep understanding of search intent. Search intent is a term that can be summed up with the question “What do search engine users want to find by searching this term?”
Let’s use the example from above. Someone who searches “rings for small fingers,” and “what’s the difference between gold and gold-filled?” are not both looking for the same thing. One wants a product, the other wants information. For the first search, a product page or a category page will best satisfy the searcher, whereas the second will likely be best satisfied by a blog post or FAQ-type page.
Understanding the different types of search intent will give you the best shot at creating content that ranks on page one of search engine results.

Combine your keyword research with your understanding of search intent, and you can create comprehensive, keyword-optimized content that provides the most relevant information to the searcher. Whether that’s a highly descriptive product description or a comprehensive blog post, you can put yourself in a better position to rank when you combine both into a comprehensive content marketing strategy.
Today, there’s evidence to show that satisfying search intent can help you outrank competitors with higher traditional search authority. In all types of search results, newer sites with fewer backlinks are trending toward the top of SERPs by providing comprehensive content that is easy to consume.
Understand your ecommerce platform
Most likely, you’re using a content management system (CMS) or ecommerce platform to host your content, like Shopify, Bigcommerce, Woocommerce, etc. SEO works no matter what CMS you’re using, but each platform can have its own specific issues you’ll need to control for.
Shopify, for example, can have issues with duplicate content and truncation of meta descriptions and titles. Searching platform-specific SEO tutorials, like Shopify SEO, may reveal the issues that other search engine optimizers have had to face when executing SEO campaigns for sites on various content management systems.
Be realistic about your competition
It’s a common misconception among ecommerce business owners that the best keywords are the most searched ones. Though they do bring the most traffic, short-tail keywords with high search volume are also highly competitive. Just take a look at the SERP for “smart keyboard.”
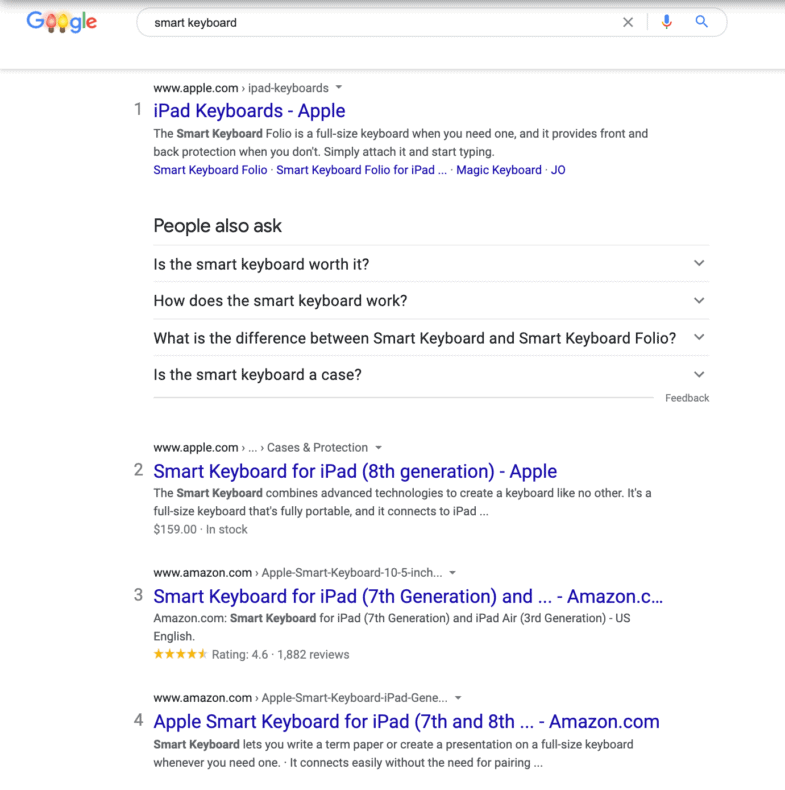
It features results from Amazon, Apple, Target, and Best Buy on page one. The term “smart keyboard” may bring in thousands of visits per month, but your chances of winning any of it are slim. Most ecommerce stores are not going to be able to compete with these brands.
This is why long-tail keywords are so valuable. Long-tail keywords are longer, more specific target keywords that may not have the same volume as short-tail keywords, but are less competitive, meaning you’re more likely to actually earn traffic from your SEO efforts.
Not only that, but long-tail keywords are more likely to draw your specific target audience. Take the example above: If you make rings for children specifically, ranking for the term “gold rings” may bring you a lot of traffic, but that traffic will likely be people looking for rings for adults. Ranking for a more specific long-tail keyword term like “gold rings for children” is more likely to bring someone to your site who is looking for your product.
Optimize site infrastructure for crawlers and users
Google ranks your content based on technical, off-page, and on-page SEO factors. Site infrastructure — the nuts and bolts of your website that affect its performance — is what technical SEO focuses on improving. To optimize the unseen parts of your ecommerce site, you should…
- Give Google specific instructions for crawling your site with a robots.txt file.
- Show Google where to find all your pages by submitting an XML sitemap. Though good internal linking can help crawlers find all your pages, there’s still a chance a page gets missed, and left off SERPs as a result. An XML sitemap ensures this doesn’t happen.
- Use canonical tags on duplicate content. If you have the same or similar content with two different URLs, canonical tags will tell Google which to crawl and index. Though you won’t get penalized for duplicate content, it can result in Google indexing the wrong page in search results, which can divide your SEO authority between multiple pages.
- Prioritize site speed (this is an official ranking factor) to ensure optimal UX. Users will abandon a page that takes longer than a few seconds to load.
- Make your ecommerce site structure easy to navigate. Your homepage should be the launchpad to the rest of your site, and internal linking should be organized from broad sources of information to more specific, ie, the homepage links to a product category pages, which links to specific product pages, which contain specific product variation pages. Site architecture has a big impact on both usability and crawlability.
- Make the mobile user experience a priority. Google has committed to mobile-first indexing, meaning it will crawl and index the mobile version of your site first. If you don’t have a mobile version, expect it to negatively affect your search rankings. Mobile ecommerce sales are expected to reach 2.91 trillion by the end of the year.
- Structure your data with schema markup. Schema markup is a way of labeling your data to better organize it for search engines. With it, you can create rich snippets for search engine results pages, which are more robust search results that can include additional content, like images, ratings, deep links, and customer reviews
Though on-page and off-page SEO account for a large portion of your SEO strategy, technical SEO is what ensures all your content and outreach efforts don’t go to waste.
Execute link-building strategies
Backlinks are still among the biggest effectors of SEO. To Google, they’re like upvotes. The more high-quality backlinks your site has, the better Google’s algorithm perceives it to be.
Link-building strategies are ones that aim to earn links from other sites back to yours. For ecommerce brands, some great ways to generate links are with influencer marketing, social media marketing, brand partnerships, and even guest blogging (yes, blogging is for ecommerce brands, too).
Don’t forget the little things
Covering the major ecommerce SEO issues should be your priority, but it shouldn’t be your only goal. Even little SEO efforts can move the needle when they’re made consistently over a long period of time. Here are some you shouldn’t skimp on:
Optimize your image alt text and file names
This is really quick and easy to do, so there’s no reason to skip it. Before you upload your images, name them something short but descriptive, as if you were to title your image in just a few words. Format this file name with dashes between words. Like this: “ecommerce-seo-best-practices.png.”
Image alt text can be easily added in your CMS once you upload your image. When you’re writing it, write in a complete sentence, and write the sentence as though you were describing it to someone who could not see it.
Make your meta descriptions and meta titles compelling and informational
Though they don’t affect ranking directly, these pieces of content are what visitors see on search engine results pages. They do directly impact SERP CTR (click-through rate), which many expert SEOs believe to be a ranking factor. Your title should compel visitors to click with good headline science, and the meta description should elaborate on the title to inform visitors of what they’ll see when they click through.
Organize your content effectively with headers
Satisfying search intent is more than giving the visitor what they’re searching for. It’s also about giving them what they’re looking for as efficiently as possible. Your content should be organized with one HTML title tag (page title), and different levels of headers below it (H2, H3, H4).
This hierarchy helps both search engines and visitors understand how pieces of content relate to each other. And it also makes it easy to skim. This isn’t just for blog content, but product pages, product descriptions, and product category pages too.
Get a complimentary ecommerce SEO audit
Implementing an ecommerce SEO strategy can seem daunting, but it really comes down to one simple principle: Do what’s best for the user, and better search rankings will follow.
Want to see how you’re doing with ecommerce SEO? Get an instant SEO audit below. Or, schedule a free consultation to see how intent SEO can boost traffic revenue by 700%.